-sharpinclude <cstdio>
-sharpinclude <cstring>
-sharpinclude <string>
using namespace std;
-sharpdefine SPLIT_SIZE 1048576
-sharpdefine BUFFER_SIZE 1000
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
printf("rcpkg - resource packager for C/CPP(GNU), created by DL.\n");
// check commands
if (argc < 4)
{
printf("Usage: rcpkg input_file_name output_library_name output_directory.\n");
return 0;
}
// check gcc
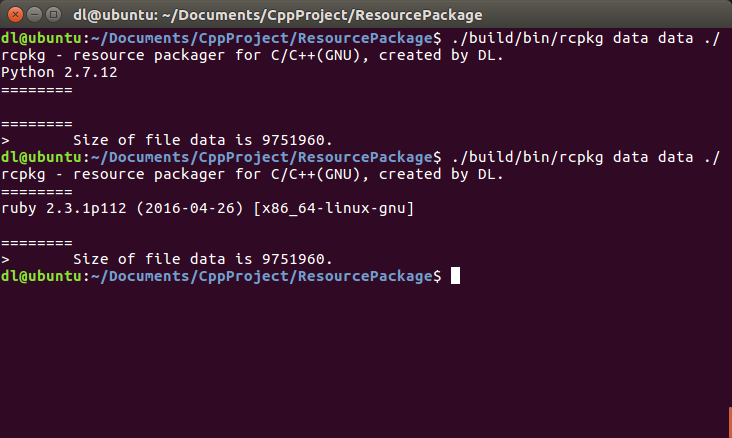
// FILE* gcc = popen("ruby -v", "r");
FILE* gcc = popen("python --version", "r");
if (!gcc)
{
printf("Cannot execute command.\n");
return 0;
}
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
string res = "";
while(memset(buffer, 0, BUFFER_SIZE - 1), fgets(buffer, BUFFER_SIZE - 1, gcc) != 0)
res += buffer;
printf("========\n%s\n========\n", res.c_str());
pclose(gcc);
// open file
FILE* input = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
if (!input)
{
printf("Cannot open file %s.\n", argv[1]);
return 0;
}
fseek(input, 0, SEEK_END);
auto fs = ftell(input);
fseek(input, 0, SEEK_SET);
printf(">\tSize of file %s is %ld.\n", argv[1], fs);
fclose(input);
return 0;
} execute the command "python-- version" with popen, but you can"t read the result with fgets, but change the command to "ruby-v" and everything will be fine. Why?